- cordycepsfuel@gmail.com
- Dighi Kala West, Hajipur, Bihar-844101, India

The Caterpillar Medicinal Mushroom: Yarsagumba Cordyceps Sinensis
Cordyceps is a genus of ascomycete fungi comprising approximately 600 species. Most Cordyceps species are endoparasitoids, mainly parasitizing insects and arthropods, making them entomopathogenic fungi. These fungi are found worldwide, with a significant concentration in Asia, particularly in Nepal, China, Japan, Bhutan, Korea, Vietnam, and Thailand. They are abundant in humid temperate and tropical forests.
Among them, Yarsagumba (Cordyceps sinensis) is one of the most well-known species. It parasitizes the ghost moth caterpillar (Hepialis aromoricanis) and forms a stroma or fruiting body. The club-shaped mycelia represent the fungal growth, while the caterpillar forms its base. Used in Tibetan traditional medicine since the 15th century, it is popularly known as Dong Chong Xia Cao in China, Yartsa Gunbu in Tibet, Tockukaso in Japan, Yarsagumba in Nepal, Keerajadi in India, and the Cordyceps Caterpillar Fungus in English.
Historical Development
Mushrooms have been integral to human history as food, medicine, and even in religious rituals for thousands of years. Cordyceps has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for over 2,000 years. Wang Ang first documented it in Ben Cao Bei Yao in 1694. In 1878, Italian scholar Saccardo officially named it Cordyceps sinensis (Berk.) Sacc.
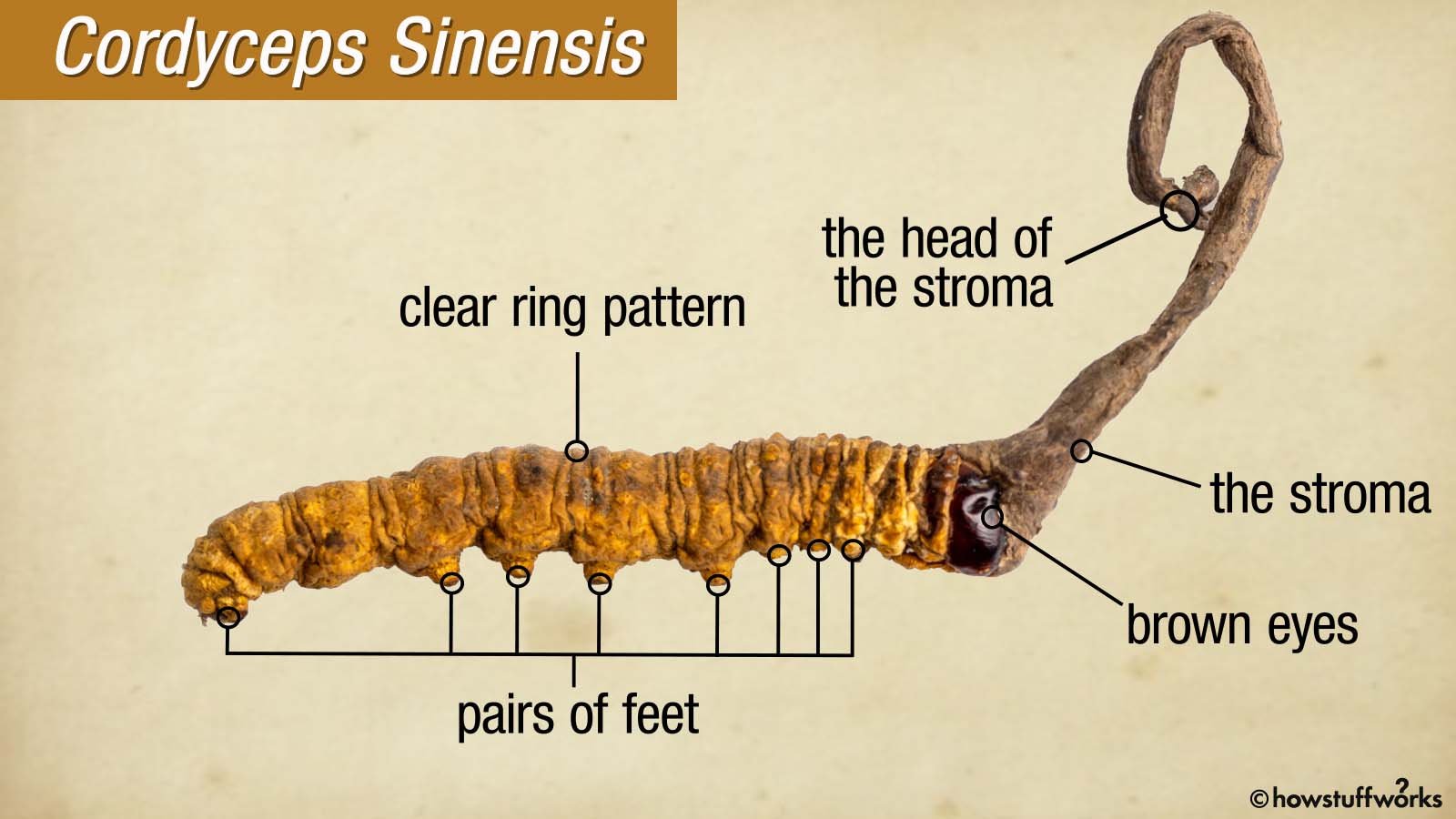
Yarsagumba Cordyceps Sinensis: A Medicinal Powerhouse
Yarsagumba Cordyceps Sinensis is a unique entomopathogenic fungus that thrives in high-altitude Himalayan meadows above 3,800 meters. The natural herbal product consists of the fruiting body and the parasitized host larva. Spores of Cordyceps caterpillar fungus germinate inside caterpillars, filling them with hyphae and producing a stalked fruiting body.
The mature Cordyceps mushroom features a dark brown to black fruit body, while the pervaded larval root is yellowish-brown. The host caterpillars typically remain about 6 inches (ca. 15 cm) underground before the fungus matures, consuming over 90% of the insect and mummifying it. The weight of a single Cordyceps specimen ranges between 300 and 500 mg.
Economic Importance
Globally, forests provide income and food security for around 1.6 billion people, including 60 million indigenous communities. Yarsagumba Cordyceps Sinensis is highly valuable, and its collection from the Himalayan regions of Bhutan, China, India, and Nepal has significantly boosted the local economy. The demand for Cordyceps caterpillar fungus has surged in the past two decades due to its increasing popularity in herbal and pharmaceutical industries.
Medical and nutritional benefits

Cordyceps is widely used as an adaptogen and immune booster, supporting kidney and lung health. Traditional uses include the following treatments:
- Respiratory ailments such as asthma, bronchitis, and tuberculosis
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Sexual dysfunction
- Liver and kidney disorders
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Athletic performance enhancement
- Aging-related conditions
The beneficial substances in yarsagumba cordyceps sinensis include cordycepin and cordycepic acid, as well as polysaccharides like beta-glucans that help boost the immune system. It also contains essential amino acids, vitamins (E, K, B1, B2, B12), proteins, sterols, and minerals such as magnesium, iron, copper, manganese, zinc, selenium, and phosphorus.
Collection & Commercialization
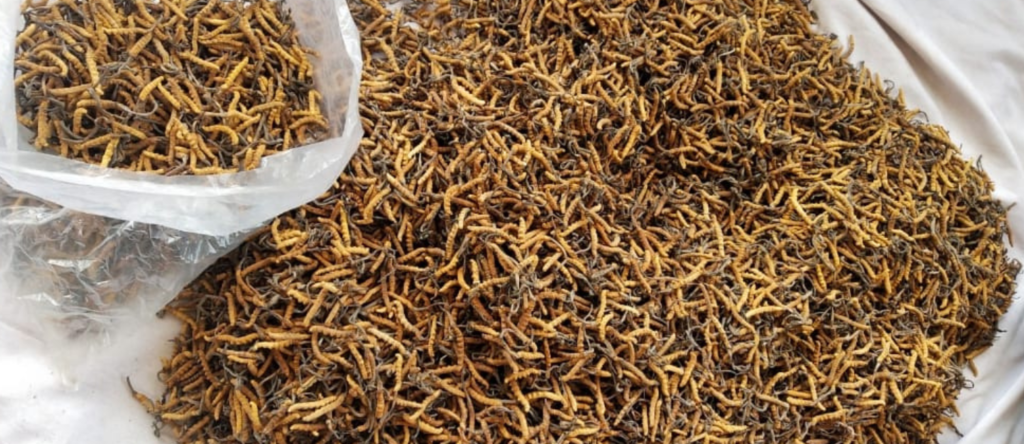

For the past 20–25 years, yarsagumba (Cordyceps sinensis) has been a significant source of income for rural communities in Bhutan, China, India, and Nepal. The harvesting season begins in spring when the snow melts and lasts for about two months. The global production of Cordyceps caterpillar fungus ranges between 84.2 and 182.5 tons per year, with significant variations in different Himalayan regions.
In India, yarsagumba (Cordyceps sinensis) is primarily found in North Sikkim and the Pithoragarh region of Uttarakhand. The international market values a single piece at approximately USD 6.77, while in India, it is locally available for around INR 100 per piece. Local traditional healers use it alone or in combination with other medicinal herbs to treat various ailments based on empirical knowledge.
Cultivation Technology
In India, Cordyceps is commonly known as Kiraghas. It was first successfully cultivated on lab iin China in 2013. Growing it needs a liquid solution with specific nutrients like glucose, sucrose, peptone, yeast powder, KH₂PO₄, MgSO₄·7H₂O, and vitamin B₁, kept at a pH level that is good for fungus to grow at 24°C.
Conclusion
Cordyceps caterpillar fungus, specifically yarsagumba Cordyceps sinensis, is a rare yet highly valuable medicinal fungus found in high-altitude Himalayan regions. It has been traditionally used to treat over 21 ailments, including cancer, bronchial asthma, diabetes, erectile dysfunction, and liver disorders. Additionally, it enhances energy, stamina, libido, and overall vitality. Research has shown its promising effects in suppressing tumor cells, but more clinical trials are necessary to establish its efficacy in modern medicine.
Featured News
CordycepsFuel: Redefining Wellness with Wild Himalayan Cordyceps Mushroom
The Science Behind Caterpillar Fungus: Bioactive Compounds Explained
August 11, 2025
The Science Behind the Healing Power of Himalayan Caterpillar Fungus
August 11, 2025
Category
Have Any Question?
Feel free to message us anytime! We are available 24/7 and always happy to assist you. Whether you have questions about cordyceps or need help with your order, we are just a message away. Your satisfaction is our priority!
- +916207920700
- cordycepsfuel@gmail.com
